Graph Sampling Language(GSL)
简介
GNN发展至今,有一套相对成熟的编程范式。我们将一个GNN模型的开发分为两个阶段:图模式的数据处理部分和神经网络部分。
神经网络部分,我们可以借助成熟的DL框架,如TensorFlow、PyTorch。
如何简单高效的描述和实现适合GNN的图数据访问模式,以及如何与主流的深度学习框架对接,是GL重点关注的。
实际中的图由于规模原因,采样是必要阶段。总结下来,图采样大致包含几类:
遍历型(Traverse),从图上获取一个batch的点或边数据;
关系型(Neighborhood,Subgraph),获取点的N跳邻域或生成由点构成的子图,用于构造训练样本;
负采样(Negative),与关系型相对,一般用于无监督训练场景,产生负例样本;
我们把如上几类操作抽象成了一套接口,称为 GSL。
开发者可以基于GSL描述用于GNN的图数据流,例如,针对“用户点击商品”异构图场景,“随机采样64个user,并按边的权重为每个user采样10个关联商品”,
可以写成g.V("user").batch(64).outV("click").sample(10).by("edge_weight")
GSL考虑实际图数据的特点,覆盖了对超大图、异构图、属性图的支持,语法设计贴近Gremlin形式,便于理解。
GSL语法
我们把一个由GSL描述的语句称为Query,一个Query通常由SOURCE、STEP和SINK三种类型的操作组成。
其中,SOURCE为查询语句的入口,表示从哪些数据出发;STEP为查询过程中游走和采样的路径,SINK为对执行结果的封装。
在GSL中,一条Query必须包含一个SOURCE和一个SINK操作。
SOURCE
V/E
SOURCE是查询语句的入口,支持 V() 和 E() 两个接口,分别表示从顶点和从边开始查询。具体如下。
def V(t, node_from=gl.NODE)
"""
Args:
t(string): 顶点类型或边类型,后续操作会针对该类型的顶点进行;
node_from: gl.NODE | gl.EDGE_SRC | gl.EDGE_DST,分别为对指定的顶点类型遍历,对指定边类型的源顶点遍历,对指定边类型的目的顶点遍历。
"""
def E(edge_type, reverse=False)
"""
Args:
edge_type(string): 边类型,后续操作会针对该类型的边进行;
reverse(boolean): 是否遍历反向边,默认为False,及遍历原始的边。
"""
无向边遍历
构图时添加边,指定为无向边。
g.edge(source, (src_type, dst_type, edge_type), decoder, directed=False)
遍历时有几下几种情况:
(1)src_type和dst_type一致,如边类型为(“item”, “item”, “i2i”),当i2i为无向边时,边会增加一份dst到src的连接,同时去重。
原始i2i数据 加载到图中的i2i数据
item item -> item item
1 2 1 2
2 1 2 1
1 3 1 3
2 3 3 1
3 3 2 3
1 4 3 2
3 3
1 4
4 1
g.E("i2i"): 遍历double and unique的i2i数据,如上”加载到图中的i2i数据 “。
g.E("i2i", reverse=Ture): 不支持,因为这时候i2i是无向边,不区分正向和反向。
(2)src_type和dst_type不一致,如边类型为(“user”, “item”, “u2i”),当u2i为无向边时,在加载时实际上除了加载原始的u2i边之外,额外加载了一份i2u的反向边。
原始u2i数据 加载到图中的u2i数据 + 加载到图中的i2u数据
user item -> user item item user
1 2 1 2 2 1
2 1 2 1 1 2
1 3 1 3 3 1
2 3 2 3 3 2
3 3 3 3 3 3
1 4 1 4 4 1
g.E("u2i"): 遍历”加载到图中的u2i数据 “,即原始数据。
g.E("u2i", reverse=Ture): 遍历“加载到图中的i2u数据”,即反向数据。
batch
当从图获取数据时,batch()用于指定每次获取到的V()或E()的多少。若同时要对数据进行shuffle(),注意在batch()之后。当shuffle(traverse=True)时,如果剩余数据不足batch_size但不为0,则返回实际数据,此时不会触发OutOfRangeError。只有剩余数据为0时,才会OutOfRangeError。
def batch(batch_size):
"""
Args:
batch_size(int): 每次获取的源数据的多少。
"""
shuffle
batch之后可以接 shuffle。 shuffle() 为可选接口,当从图获取数据时,表示是否要对顶点/边进行随机获取。
def shuffle(traverse=False):
"""
Args:
traverse(boolean): 是否要随机获取数据源,默认False。
True表示按序遍历,当遍历到结尾时会触发OutOfRangeError,False则不会OutOfRangeError。
"""
示例
(1)顺序遍历图中的user顶点,batch size为64,当遍历完全图user顶点后,OutOfRange。
query = g.V("user").batch(64).alias('seed').values()
ds = gl.Dataset(query)
while True:
try:
ds.next()
except gl.OutOfRangeError:
break
(2)随机有放回地遍历64个user类型的顶点。永远不会OutOfRange。
query = g.V("user").batch(64).shuffle().alias('seed').value()
ds = gl.Dataset(query)
for i in range(100):
ds.next()
(3)随机无放回地遍历64个user类型的顶点,当遍历完全图的user顶点后,OutOfRange。
query = g.V("user").batch(64).shuffle(traverse=True).alias('seed').values()
ds = gl.Dataset(query)
while True:
try:
ds.next()
except gl.OutOfRangeError:
break
通过E遍历边的方式类似。
STEP 图采样/负采样
STEP用于描述查询游走的路径和采样的方式。一条查询语句中可以包含0到多个STEP。目前,STEP包含以下两类接口:描述路径游走,描述采样方式。一个完整的STEP包含游走+采样(图采样或负采样)。
描述路径游走的接口,表示当前操作对象的转移。例如,g.V()表示当前操作对象为顶点,可以通过outE()把当前操作对象转移到顶点的出边上,后面的操作表示针对边来进行。当边的操作结束后,可以通过inV() / outV(),再将焦点转移到边对应的目的顶点或源顶点上。
(1)游走接口:
def inV():
""" 承接边(只能跟在边操作之后),表示两个顶点中箭头指向的那个,即目的顶点
"""
def outV():
""" 承接边(只能跟在边操作之后),表示两个顶点中箭头发起的那个,即源顶点
"""
def inE(edge_type):
""" 承接顶点(只能跟在顶点操作之后),表示顶点的入边
Args:
edge_type(string): 边的类型,当该边为有向边时, 调用inE报错
"""
def outE(edge_type):
""" 承接顶点(只能跟在顶点操作之后),表示顶点的出边
Args:
edge_type(string): 边的类型
"""
def inV(edge_type):
""" 承接顶点(只能跟在顶点操作之后),表示顶点沿着边的上游顶点
Args:
edge_type(string): 边的类型,当该边为有向边时, 调用inV报错
"""
def outV(edge_type):
""" 承接顶点(只能跟在顶点操作之后),表示顶点沿着边的下游顶点
Args:
edge_type(string): 边的类型
"""
def outNeg(edge_type):
""" 承接顶点(只能跟在顶点操作之后),表示在该边类型下负采样下游顶点
Args:
edge_type(string): 边的类型
"""
def inNeg(edge_type):
""" 承接顶点(只能跟在顶点操作之后),表示在该边类型下负采样上游顶点
Args:
edge_type(string): 边的类型,当该边为有向边时, 调用inNeg报错
"""
(2)采样接口:
描述采样方式的接口,在前序路径描述的基础上,且当前操作对象为顶点时,如何采样该类型的顶点作为前序顶点的邻居,包括采样多少、采样策略。
def sample(N):
""" 承接顶点(只能跟在顶点操作之后),表示当前顶点采样多少作为前序顶点的邻域
Args:
N(int): 采样的数量
"""
def by(strategy):
""" 紧跟sample()之后,表示采样策略
Args:
strategy(string): 采样策略
如果前序路径为采样,支持的策略包括:
“edge_weight”, "in_degree", "topk", "random", "full";
如果前序路径为负采样,支持的策略包括:
"in_degree", "random", "node_weight"
"""
图游走
outV(edge_type)/outE(edge_type):从边的源顶点开始到目的顶点向前推进,即源顶点沿着其出边游走。
inV(edge_type)/inE(edge_type):从边的目的顶点开始到源顶点向后回溯,即目的顶点沿着入边游走。其中,edge_type对应的边必须为无向边(在构图时,必须指定directed=false,即可以反向游走,参考 图对象)。
例如,对于如下所示异构图,从user顶点开始,沿u2i边采样user的一跳邻居,再沿i2i边采样user的二跳邻居。
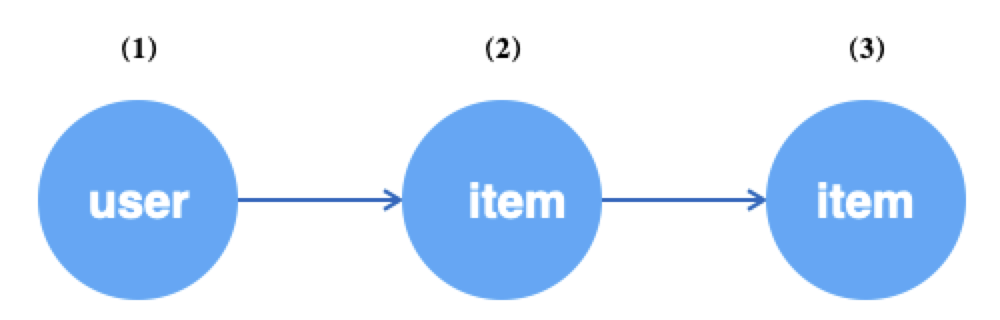
g.V("user").batch(64).alias('src') # (1) 获取64个user顶点
.outV("u2i").sample(10).by("edge_weight").alias('hop1') # (2) 为上述每个user采样10个邻居item
.outV("i2i").sample(15).by("random").alias('hop2') # (3) 为上述每个item采样15个邻居item
若以边为数据源,可以再获取边后分别针对其端点进行操作。一般情况下,获取边往往用于无监督学习,把边看成正样本,再对边的源顶点进行负邻居采样作为负样本。
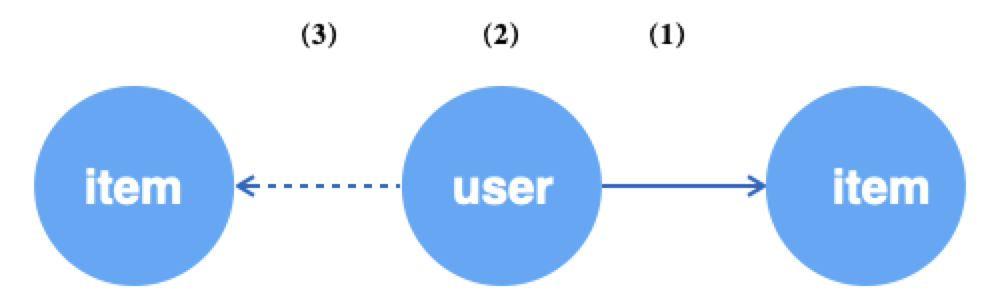
g.E("u2i").batch(64).alias('edge') # (1) 随机获取64条u2i的边
.ouV().alias('src') # (2) 跳转到边的源顶点,即user
.outNeg("u2i").sample(10).by("random").alias('neg') # (3) 为上述每个user采样10个不相关的item
当边为无向边时,可以通过outV(edge_type)和inV(edge_type)来实现循环采样,源点和目的点互为邻居。
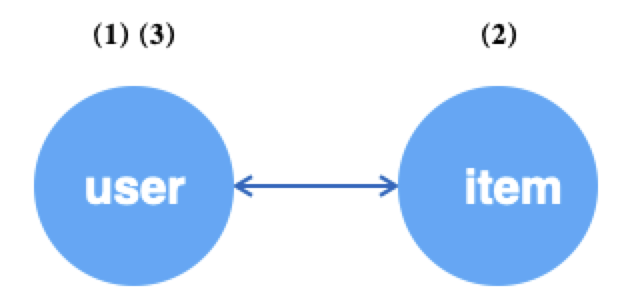
g.V("user").batch(64).alias('src') # (1) 随机获取64个user顶点
.outV("u2i").sample(10).by("random").alias('hop1') # (2) 为上述每个user采样10个邻居item
.inV("u2i").sample(5).by("random").alias('hop2') # (3) 为上述每个item采样10个邻居user
图采样
图采样的Query接口组合如下:
# 沿出边采样邻居顶点
outV(edge_type).sample(N).by(strategy)
# 沿入边采样邻居顶点
inV(edge_type).sample(N).by(strategy)
# 沿出边采样邻居边
outE(edge_type).sample(N).by(strategy)
# 沿出边采样邻居边
inE(edge_type).sample(N).by(strategy)
GL目前已支持以下几种采样策略,对应**.by**接口的strategy参数。
| strategy | 说明 |
|---|---|
| edge_weight | 以边权重为概率采样 |
| random | 有放回随机采样 |
| random_without_replacement | 无放回随机采样,邻居数不够时,参考填充规则 |
| topk | 返回边权重topK的邻居,邻居数不够时,参考填充规则 |
| in_degree | 以顶点入度为概率采样 |
| full | 邻居数不足N时,返回全部邻居,大于N时,以N截断 |
填充规则:当采样要求的数据不足时,需要以某种方式填充返回结果。默认情况下,用default_neighbor_id填充补齐不足的id,default_neighbor_id默认为0,可以通过gl.set_default_neighbor_id(xx)来设置。如要循环填充,即循环使用已有邻居id而非default_neighbor_id,则设置填充模式gl.CIRCULAR,gl.set_padding_mode(gl.CIRCULAR)。
示例:
以下示例表示以64的batch size遍历图中的“用户“顶点,并按照“购买”边的权重为采样概率,对每个“用户”采样10个“用户”“购买”的“商品”。
g.V("user").batch(64).alias("u") \
.outV('buy').sample(10).by("edge_weight").alias("1hop")
负采样
负采样的Query接口组合如下:
# 沿出边采样负邻居顶点(.where表示加上条件的负采样)
outNeg(edge_type).sample(expand_factor).by(strategy)[.where(target, condition={})]
# 沿入边采样负邻居顶点(.where表示加上条件的负采样)
inNeg(edge_type).sample(expand_factor).by(strategy)[.where(target, condition={})]
# 顶点表负采样
Neg(node_type).sample(expand_factor).by("node_weight")
sample接口的参数expand_factor,表示对每个顶点采样做少个负样本。
GL目前已支持以下几种负采样策略,对应**.by**接口的strategy参数。
| strategy | 说明 |
|---|---|
| random | 随机负采样,不保证true-negative |
| in_degree | 以顶点入度分布为概率进行负采样,保证true-negative |
| node_weight | 按照顶点权重在顶点表负采样,仅适用于Neg(node_type) |
where参数使用:
def where(target, condition={}):
""" Add condition for negative samlpler. Used after `by`.
Args:
target (string): Alias of upstream which is the postive sample
that condition should match.
condition (dict, optional): Keys are as following.
"batch_share" (bool, optional): Whether sampled negative samples are
shared by this batch. Defaults to False.
"unique" (bool, optional): Whether sampled negtive samples are unique.
Defaults to False.
"int_cols" (int list, optional): int columns as condition.
Defaults to []. 表示在这些指定的属性下进行负采样。
比如target的int属性有3个,int_cols=[0,1]表示,在第一个int属性和target的第1个
int属性一样的节点,以及第2个int属性和target的第2个属性一样的节点里选取负样本。
"int_props" (float list, optional) : proportions of int columns.
Defaults to []. 表示int_cols里每个属性采样的比例。
比如int_cols=[0,1],int_props=[0.1,0.2],表示在和target的第1个int属性一样的点
里采样expand_factor*0.1个负样本,在和dst_ids的
第2个int属性一样的点里采样expand_factor*0.2个负样本。
"float_cols" (int list, optional): float columns as condition.
Defaults to [].
"float_props" (float list, optional): proportions of float columns.
Defaults to [].
"str_cols" (int list, optional): string columns as condition.
Defaults to [].
"str_props" (float list, optional): proportions of string columns.
Defaults to [].
"""
Note:
Decoder中attr_types描述为(“string”, Size)的属性,在condition中看做int属性。
int_props, float_props, str_props中的每一项必须为float类型,即如[1]需要写成[1.0]
示例:
以下示例表示以64的batch size遍历图中的“用户“顶点,并对每个“用户”随机采样10个“用户”“未购买”的“商品”。
g.V("user").batch(64).alias("u") \
.outNeg('buy').sample(10).by("random").alias("1hop") \
.values()
以下示例表示以64的batch size遍历图中的“购买“边,并对边上每个“用户”按条件采样10个“用户”“未购买”的“商品”,其中“商品”需要满足的条件是,和“用户”的第1个int属性相同的“商品”采样100.25个,和“用户”的第2个int属性相同的“商品”采样100.25个,和“用户”的第1个str属性相同的“商品”采样10*0.5个:
g.E("buy").batch(64).alias("e").each(
lambda e: (
e.inV().alias('dst'),
e.outV().alias('src') \
.outNeg("buy").sample(10).by('random').where(
"dst",
condition={
"int_cols": [0,1], "int_props": [0.25,0.25],
"str_cols": [0], "str_props": [0.5]}).alias('neg'))) \
.values()
多路下游
each
一个典型的GNN算法对图数据的需求往往是多路的。each()接口用于表达Query的多分枝,当进行到某个阶段后,针对前序结果(可能有多个)分别进行不同的操作。
def each(func):
"""
Args:
func(lambda): 构造子query的lambda表达式,表达式的输入为紧跟上游操作的输出。
Return:
Query对象
"""
例如,在二部图(user-item-item)GraphSAGE算法中,我们为了学习user和item在同一空间下的相似性,首先会随机获取图的u2i边作为训练的正样本,再对边的源点(即user顶点)采样其负邻居(item顶点)产生负样本。user通过一阶邻居进行编码(把邻域信息聚合到中心节点),即需要采样其一跳邻居。item也需要一阶邻居来编码。图数据的访问模式如下所示。
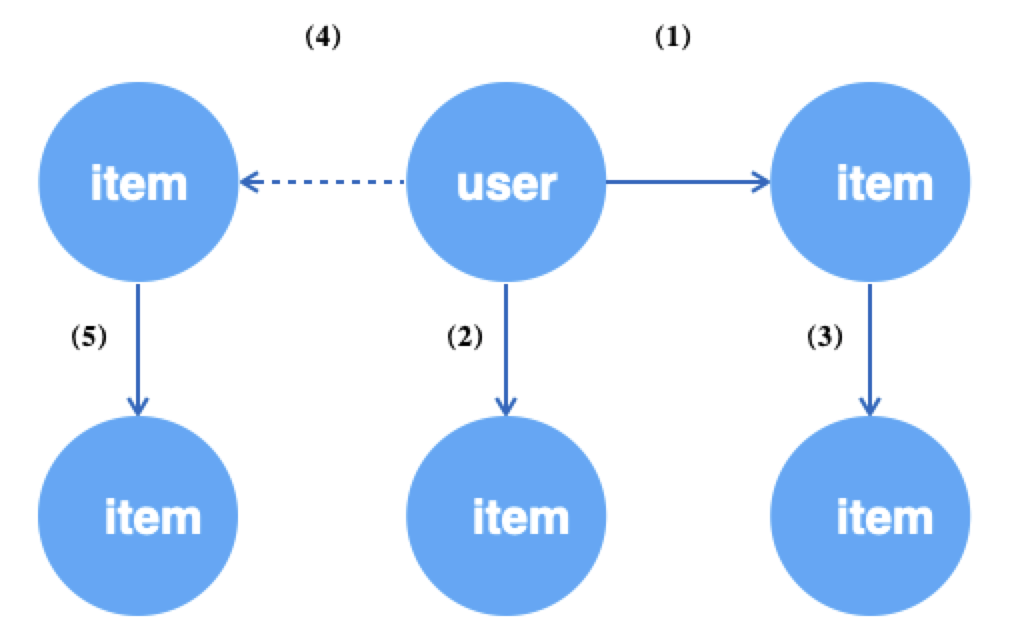
query = g.E("u2i").batch(512).shuffle().alis('edge') # (1) 随机获取512条u2i的边
.each(lambda edge: # 上游输出的是边
(edge.outV().alias('src').each(
lambda src:
(src.outV("u2i").sample(10).by("edge_weight").alias('src_1hop'), # (2) 为边的源顶点user采样10个邻居
src.outNeg("u2i").sample(5).by("in_degree").alias('src_neg') \ # (4) 为边的源顶点user负采样5个邻居
.outV("i2i").sample(10).by("random").alias('src_neg_1hop')), # (5) 为上述负采样的每个item采样其10个邻居
edge.inV().alias('dst').outV("i2i").sample(10).by("random").alias('dst_1hop') # (3) 为边的目的顶点item采样10个邻居
).values()
变量
each接口用lambda function对上游进行多路下游操作。也可以将上游赋值给一个变量,用该变量接多路下游。
Note: 从同一个SOURCE游走的任意STEP,后面接**.values()**都表示这个Query描述完成。从同一个SOURCE游走的任意STEPs只能接一次vlaues(). 如下示例的第19行,edge.values()和src.values() / dst.values() 等价。
# 采样边
edge = g.E("u2i").batch(512).shuffle().alias(...)
# 获取边的源顶点
src = edge.outV().alias('src')
# 获取边的目的顶点
dst = edge.inV().alias('dst')
# 给源顶点采样邻居
src.outV("u2i").sample(10).by("edge_weight").alias('src_1hop')
# 给源顶点做负采样
src.outNeg("u2i").sample(5).by("in_degree").alias('src_neg')
.outV("i2i").sample(10).by("random").alias('src_neg_1hop'))
# 给目的顶点采样邻居
dst.outV("i2i").sample(10).by("random").alias('dst_1hop')
query = edge.values()
命名
alias
每一个SOURCE或STEP都需要由alias命名,便于后续对输出结果的访问。
def alias(name):
"""
Args:
name(string): 给操作起一个别名。
Return:
Query对象
"""
SINK
values
一句Query描述完Source、Step后,需要以.values()结尾,表示Query描述完整。Query中的任意一个节点.values()都表示该query结束。如:
query1 = g.E("u2i").batch(512).shuffle().alias("edges")
.values()
src = g.V("user").batch(64).alias("src")
dst = src.outV("u2i").sample(5).by("random").alias('dst')
query2 = src.values() # 等价于query2 = dst.values()
GSL执行结果
GSL表达的Query以遍历图中的顶点或边开始,因此可以循环地执行。 GSL执行的结果是Query中描述的所有游走的顶点或边构成的对象,他们包含了自身的id和属性、标签、权重。
Dataset
graphlearn.Dataset接口,用于将Query的结果构造为Numpy组成的graphlearn.Nodes/graphlearn.Edges或graphlearn.SparseNodes/graphlearn.Edges对象的生成器。Nodes等对象描述详见文档 数据对象
class Dataset:
def __init__(self, qeury, window=10):
"""
query: GSL query, 从g.V()/g.E()开始,以.values()结束
window: Dataset会进行异步地预取数据,window为预取数据的大小。
"""
def next(self):
"""
返回一个dict,其中,key为Dataset对应的GSL query中的每一个alias,
value为alias对应的Nodes或Edges的数据。
*V()对应Nodes,*E()对应Edges。
特殊地,full采样对应的输出为SparseNodes或SparseEdges。
"""
使用方式如下:
import graphlearn as gl
query = g.V("user").batch(64).alias('u') \
.outV('buy').sample(10).by('random').alias('i') \
.outE('i2i').sample(5).by('random').alias('i-i')
.values()
ds = gl.Dataset(query)
while True:
try:
res = ds.next()
except gl.OutOfRangeError:
break
上例中,Dataset.next()的输出如下。
res = ds.next()
# { "u": Nodes, 'i': Nodes, 'i-i': Edges}
res["u"].ids
# Int64 np array, shape: [64]([batch_size])
res["u"].int_attrs
# Int64 np array, shape: [64, 2]([batch_size, int_attr_num]) or None
res["u"].float_attrs
# Float np array, shape: [64, 3]([batch_size, float_attr_num]) or None
res["u"].string_attrs
# String np array, shape: [64, 1]([batch_size, string_attr_num]) or None
res["u"].weights
# Float np array, shape: [64]([batch_size]) or None
res["i"].labels
# Int32 np array, shape: [64]([batch_size]) or None
res["u"].ids
# Int64 np array, shape: [64, 10]([batch_size, nb_count])
res["u"].int_attrs
# Int64 np array, shape: [64, 10, 2]([batch_size, nb_count, int_attr_num]) or None
res["u"].float_attrs
# Float np array, shape: [64, 10, 5]([batch_size, nb_count, float_attr_num]) or None
res["u"].string_attrs
# String np array, shape: [64, 10, 3]([batch_size, nb_count, string_attr_num]) or None
res["u"].weights
# Float np array, shape: [64, 10]([batch_size, nb_count])
res["i"].labels
# Int32 np array, shape: [64, 10]([batch_size, nb_count])
res["i-i"].src_ids
# Int64 np array, shape: [64 * 10, 5]([batch_size, nbr_count])
res["i-i"].dst_ids
# Int64 np array, shape: [64 * 10, 5]([batch_size, nb_count])
res["i-i"].int_attrs
# Int64 np array, shape: [64 * 10, 5, 1]([batch_size, nb_count, int_attr_num]) or None
res["i-i"].float_attrs
# Float np array, shape: [64 * 10, 5, 1]([batch_size, nb_count, float_attr_num]) or None
res["i-i"].string_attrs
# String np array, shape: [64 * 10, 5, 2]([batch_size, nb_count, string_attr_num]) or None
res["i-i"].weights
# Float np array, shape: [64 * 10, 5]([batch_size, nb_count])
res["i-i"].labels
# Int32 np array, shape: [64 * 10, 5]([batch_size, nb_count])
示例
数据准备
vim gen_test_data.py
def gen_files():
import random
u_count = 100
i_count = 10
with open("data/user", 'w') as f:
s = 'id:int64\tweight:float\n'
f.write(s)
for i in range(u_count):
s = '%d\t%f\n' % (i, i / 10.0)
f.write(s)
with open("data/item", 'w') as f:
s = 'id:int64\tfeature:string\n'
f.write(s)
for i in range(100, 100 + i_count):
s = '%d\t%s:%d:%f:%f:%s\n' % (i, str(i) + 's', i, i*1.0, i * 10.0, 'x')
f.write(s)
with open("data/u-i", 'w') as f:
s = 'src_id:int64\tdst_id:int64\tweight:float\n'
f.write(s)
for i in range(u_count):
for j in range(100, 100 + i_count):
s = '%d\t%d\t%f\n' % (i, j, (i + j) * 0.1)
f.write(s)
gen_files()
执行脚本
mkdir -p data
python gen_test_data.py
**图对象构建和GSL执行 **本示例中“buy”边为无向边。
vim test_local.py
import os
import sys
import graphlearn as gl
def test_node_iterate(graph):
"""Iterate users, sample 2 hops with path user-(buy)-item-(buy_reverse)-user.
"""
query = graph.V("user").batch(32).shuffle(traverse=True).alias("src") \
.outV("buy").sample(5).by("edge_weight").alias("hop1") \
.inE("buy").sample(2).by("random").alias("hop1-hop2") \
.inV().alias("hop2") \
.values()
ds = gl.Dataset(query)
epoch = 2
for i in range(epoch):
step = 0
while True:
try:
res = ds.next()
step += 1
src_nodes = res["src"]
hop1_nodes = res["hop1"]
hop1_hop2_edges = res["hop1-hop2"]
hop2_nodes = res["hop2"]
assert isinstance(src_nodes, gl.Nodes)
assert isinstance(hop1_nodes, gl.Nodes)
assert isinstance(hop1_hop2_edges, gl.Edges)
assert isinstance(hop2_nodes, gl.Nodes)
assert src_nodes.type == "user"
assert hop1_nodes.type == "item"
assert hop1_hop2_edges.type == ("item", "user", "buy_reverse")
assert hop1_hop2_edges.edge_type == "buy_reverse"
assert hop2_nodes.type == "user"
if step == 100 // 32 + 1: # total user nodes count is 100
assert tuple(src_nodes.ids.shape) == (100 % 32, )
assert tuple(hop1_nodes.ids.shape) == (100 % 32, 5)
assert tuple(hop1_hop2_edges.src_ids.shape) == (100 % 32 * 5, 2)
assert tuple(hop1_hop2_edges.dst_ids.shape) == (100 % 32 * 5, 2)
assert tuple(hop2_nodes.ids.shape) == (100 % 32 * 5, 2)
assert tuple(hop1_nodes.float_attrs.shape) == (100 % 32, 5, 2) # 2 float attrs
assert tuple(hop1_hop2_edges.weights.shape) == (100 % 32 * 5, 2)
assert tuple(hop2_nodes.weights.shape) == (100 % 32 * 5, 2)
else:
assert tuple(src_nodes.ids.shape) == (32, )
assert tuple(hop1_nodes.ids.shape) == (32, 5)
assert tuple(hop1_hop2_edges.src_ids.shape) == (32 * 5, 2)
assert tuple(hop1_hop2_edges.dst_ids.shape) == (32 * 5, 2)
assert tuple(hop2_nodes.ids.shape) == (32 * 5, 2)
assert tuple(hop1_nodes.float_attrs.shape) == (32, 5, 2) # 2 float attrs
assert tuple(hop1_hop2_edges.weights.shape) == (32 * 5, 2)
assert tuple(hop2_nodes.weights.shape) == (32 * 5, 2)
except gl.OutOfRangeError:
break
def test_edge_iterate(graph):
"""Iterate buy edges, sample hops of src and dst nodes.
user-(buy)-item (1) iterate edges
| |
(buy) (buy_reverse)
| |
item user (2) sample neighbors of src and dst nodes. `
"""
edges = graph.E("buy").batch(32).shuffle(traverse=True).alias("edges")
src = edges.outV().alias("src")
dst = edges.inV().alias("dst")
neg = src.outNeg("buy").sample(2).by("in_degree").alias("neg")
neg.inV("buy").sample(4).by("random").alias("neg_hop1")
src.outE("buy").sample(5).by("random").alias("src_hop1_edges") \
.inV().alias("src_hop1")
dst.inE("buy").sample(3).by("edge_weight").alias("dst_hop1_edges") \
.inV().alias("dst_hop1")
query = edges.values()
ds = gl.Dataset(query)
epoch = 2
for i in range(epoch):
step = 0
while True:
try:
res = ds.next()
step += 1
edges = res["edges"]
src_nodes = res["src"]
dst_nodes = res["dst"]
neg_nodes = res["neg"]
src_hop1_edges = res["src_hop1_edges"]
src_hop1_nodes = res["src_hop1"]
neg_hop1_nodes = res["neg_hop1"]
dst_hop1_edges = res["dst_hop1_edges"]
dst_hop1_nodes = res["dst_hop1"]
assert edges.type == ("user", "item", "buy")
assert src_nodes.type == "user"
assert dst_nodes.type == "item"
assert neg_nodes.type == "item"
assert src_hop1_edges.type == ("user", "item", "buy")
assert src_hop1_nodes.type == "item"
assert neg_hop1_nodes.type == "user"
assert dst_hop1_edges.type == ("item", "user", "buy_reverse")
assert dst_hop1_nodes.type == "user"
if step == 1000 // 32 + 1: # total buy edges count is 1000
assert tuple(neg_nodes.float_attrs.shape) == (1000 % 32, 2, 2)
assert tuple(neg_hop1_nodes.weights.shape) == (1000 % 32 * 2, 4, )
assert tuple(src_hop1_edges.weights.shape) == (1000 % 32, 5)
assert tuple(src_hop1_nodes.float_attrs.shape) == (1000 % 32, 5, 2)
assert tuple(dst_hop1_edges.weights.shape) == (1000 % 32, 3)
assert tuple(dst_hop1_nodes.weights.shape) == (1000 % 32, 3)
else:
assert tuple(neg_nodes.float_attrs.shape) == (32, 2, 2)
assert tuple(neg_hop1_nodes.weights.shape) == (32 * 2, 4, )
assert tuple(src_hop1_edges.weights.shape) == (32, 5)
assert tuple(src_hop1_nodes.float_attrs.shape) == (32, 5, 2)
assert tuple(dst_hop1_edges.weights.shape) == (32, 3)
assert tuple(dst_hop1_nodes.weights.shape) == (32, 3)
src_ids = list(dst_hop1_edges.src_ids.flatten())
dst_ids = list(dst_hop1_edges.dst_ids.flatten())
weights = list(dst_hop1_edges.weights.flatten())
for src_id, dst_id, weight in zip(src_ids, dst_ids, weights):
assert abs(0.1 * (src_id + dst_id) - weight) < 10 ** -6
src_ids = list(src_hop1_edges.src_ids.flatten())
dst_ids = list(src_hop1_edges.dst_ids.flatten())
weights = list(src_hop1_edges.weights.flatten())
for src_id, dst_id, weight in zip(src_ids, dst_ids, weights):
assert abs(0.1 * (src_id + dst_id) - weight) < 10 ** -6
except gl.OutOfRangeError:
break
def main(argv):
cur_path = sys.path[0]
# Step 1: Construct graph with data source.
# Edges:
# user<--(buy)-->item
g = gl.Graph()
g.node(os.path.join(cur_path, "data/user"),
node_type="user", decoder=gl.Decoder(weighted=True)) \
.node(os.path.join(cur_path, "data/item"),
node_type="item", decoder=gl.Decoder(attr_types=['string', 'int', 'float', 'float', 'string'])) \
.edge(os.path.join(cur_path, "data/u-i"),
edge_type=("user", "item", "buy"), decoder=gl.Decoder(weighted=True), directed=False) \
.init()
# Step 2: Describe the queries on graph.
test_node_iterate(g)
test_edge_iterate(g)
g.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main(sys.argv[1:])
执行脚本
>>> python test_local.py
详细的示例见代码: query_examples.py