数据源¶
本文档用以说明GraphLearn支持的数据格式,以及如何通过API来描述和解析。
数据格式¶
Graph数据可分为顶点数据和边数据。一般的,顶点数据包含顶点ID和属性,描述一个实体;边数据包含源顶点ID和目的顶点ID,描述顶点间的关系。在异构图场景中,顶点和边分别存在多种类型。因此,我们需要顶点和边的类型信息,才能对不同类型的顶点和边加以识别。类型信息通过API来描述。顶点和边都可以具有属性,比如“某用户在星期六上午购买了某商品”,时间信息“星期六上午”就是边属性。此外,很多场景用户需要“权重”的概念,或是顶点权重,或是边的权重,作为某种重要性的度量,比如“按权重进行邻居节点采样”。“权重”的来源多种多样,因任务不同而不同。在有监督学习的分类任务中,顶点或边还可能拥有标签。
我们将这些典型场景的数据格式抽象为ATTRIBUTED、WEIGHTED、LABELED,分别用于表示顶点或边包含属性的、具有权重的、具有标签的。对顶点数据源和边数据源来说,这三者可以同时存在,也可以部分存在。
基础格式¶
基础的顶点数据只包含一个顶点的ID,ID类型为bigint,每条数据代表一个顶点。很多时候只有顶点ID是不够的,还需包含属性、权重或标签。
基础的边数据只包含源顶点ID和目的顶点ID,ID类型为bigint,每条数据代表一条边,表示两个顶点之间的关系。基础边数据源的schema如下所示。
基础的边数据格式可以独立使用,即不附加属性、权重和标签。
边基础格式schema
| 域 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| src_id | BIGINT | |
| dst_id | BIGINT |
属性格式(ATTRIBUTED)¶
用于表达顶点或边的属性信息。一般情况下,顶点默认具有属性,不然只需要边表就够了。属性列只有一列,为string类型。
string内部可通过自定义分隔符分割多个属性。比如,某一顶点属性有3个,分别为shanghai, 10, 0.01,用分隔符‘:’分隔,则该顶点对应的属性数据为shanghai:10:0.01。
当数据格式具有属性时,无论是顶点数据,还是边数据,在API描述时,都需要显示指定ATTRIBUTED以告知系统。
顶点数据属性格式schema
| 域 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | BIGINT | |
| attributes | STRING |
边数据属性格式schema
| 域 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| src_id | BIGINT | |
| dst_id | BIGINT | |
| attributes | STRING | |
权重格式(WEIGHTED)¶
用于表达顶点或边带有权重的情况。权重列只有一列,为float类型。当数据格式具有权重时,无论是顶点数据,还是边数据,在API描述时,都需要显示指定WEIGHTED以告知系统。
顶点数据权重格式schema
| 域 | 数据类型 | 信息列 |
|---|---|---|
| id | BIGINT | |
| attributes | FLOAT |
边数据权重格式schema
| 域 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| src_id | BIGINT | |
| dst_id | BIGINT | |
| weight | FLOAT | |
标签格式(LABELED)¶
用于表达顶点或边带有标签的情况。标签列只有一列,为int类型。当数据格式具有标签时,无论是顶点数据,还是边数据,在API描述时,都需要显示指定LABELD以告知系统。
顶点数据标签格式schema
| 域 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | BIGINT | |
| label | INT | |
边数据标签格式schema
| 域 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| src_id | BIGINT | |
| dst_id | BIGINT | |
| label | INT | |
组合格式¶
ID是组成顶点和边数据源的必选信息,weight,label,attribute为可选信息。当同时具备WEIGHTED、ATTRIBUTED、LABELED一到多个时,在数据源中,必选信息和可选格式信息的组合需要遵循一定的顺序。
1)顶点数据源,混合格式schema的顺序如下表所示。
| 域 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| id | BIGINT | 必选 |
| weight | FLOAT | 可选: WEIGHTED |
| label | BIGINT | 可选: LABELED |
| attributes | STRING | 可选: ATTRIBUTED |
2)边数据源,混合格式schema的顺序如下表所示。
| 域 | 数据类型 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| src_id | BIGINT | 必选 |
| dst_id | BIGINT | 必选 |
| weight | FLOAT | 可选: WEIGHTED |
| label | BIGINT | 可选: LABELED |
| attributes | STRING | 可选: ATTRIBUTED |
扩展信息可选择0个或多个,同时需要保证schema的顺序维持上表顺序不变。
数据源¶
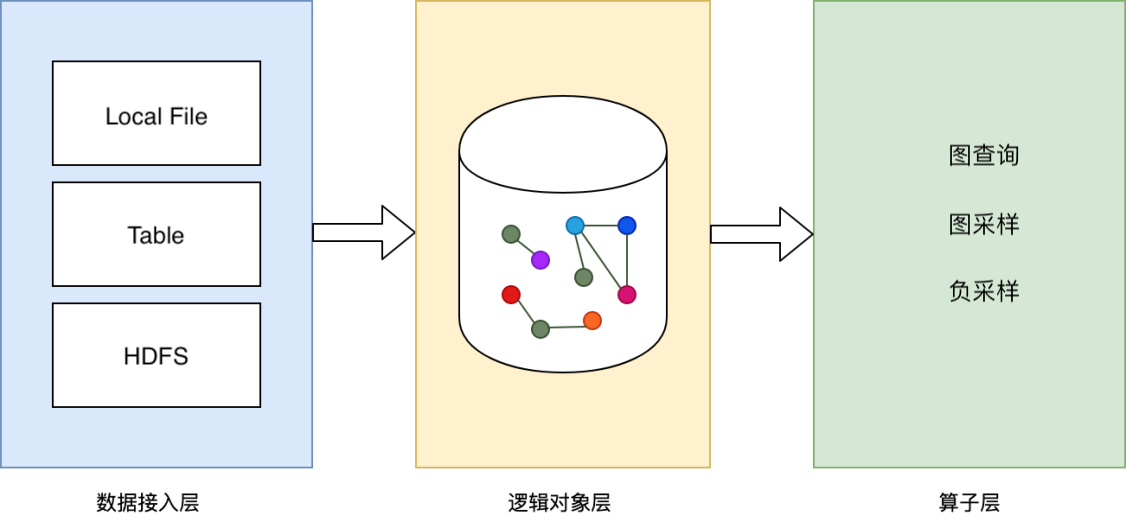 data_source
data_source
系统抽象了数据接入层,可方便对接多种类型的数据源,目前开源支持LocalFileSystem,HDFS等数据源可以mount到本地。数据表现为二维结构化,行代表一个顶点或一条边数据,列表示顶点或边的某一项信息。
Local FileSystem¶
接入本地文件/或挂载到本地的文件作为图数据源,支持文件夹、文件; 在分布式下,每个GraphLearn Server读取指定的文件的全部数据作为数据源,因此,用本地文件(包括mount到本地文件)作为分布式GraphLearn的图数据源时,需提前将原始数据做分片,为每个Server指定不同的分片作为数据源。
在本地文件中,数据类型如下。其中,列名不做要求。支持从一个或多个本地文件读取数据。
| 列 | 类型 |
|---|---|
| id | int64 |
| weight | float |
| label | int32 |
| features | string |
- 顶点文件格式。其中,第一行为列名,表示必选信息或扩展信息,以tab分隔,每一个元素为“列名:数据类型”。其余每行数据代表一个顶点的信息,与第一列的信息名对应,以tab分隔。
# file://node_table
id:int64 feature:string
0 shanghai:0:s2:10:0.1:0.5
1 beijing:1:s2:11:0.1:0.5
2 hangzhou:2:s2:12:0.1:0.5
3 shanghai:3:s2:13:0.1:0.5
2)边文件格式。其中,第一行为列名,表示必选信息或扩展信息,以tab分隔,每一个元素为“列名:数据类型”。
其余每行数据代表一条边的信息,与第一列的信息名对应,以tab分隔。
# file://edge_table
src_id:int64 dst_id:int64 weight:float feature:string
0 5 0.215340 red:0:s2:10:0.1:0.5
0 7 0.933091 grey:0:s2:10:0.1:0.5
0 1 0.362519 blue:0:s2:10:0.1:0.5
0 9 0.097545 yellow:0:s2:10:0.1:0.5
通过本地文件作为数据源,可以直接在脚本中使用文件路径。详见下一章“图对象”。
用户API¶
Decoder定义¶
Decoder类用于描述上所述数据格式,定义如下。
class Decoder(weighted=False, labeled=False, attr_types=None, attr_delimiter=":")
"""
weighted: 描述数据源是否带权重,默认为False
labeled: 描述数据源是否带有标签,默认为False
attr_types: 当数据源带属性时,该参数为一个string list,描述每一个属性的类型。
list中的每个元素仅支持"string"、"int"和"float"类型。
参数形如["string", "int", "float"],代表数据的属性列包含有3个属性,
按照顺序分别是string类型,int类型,float类型。
默认None,即数据源不带属性。
attr_delimiter: 当数据带有属性(被压缩为一个大string)时,需要知道如何解析,该参数描述各个属性间的分隔符。
如"shanghai:0:0.1",分隔符为":"。默认为":"。
attr_dims: 仅用于TF版本的图神经网络中,描述对应的离散属性编码成embeding的dimension,是一个int list。
所有有效的attr_type和attr_dim的对应关系如下:
| attr_type |attr_dim| encoded into |
| --------- | -- | -------- |
| ("string",10) | 8 | Embedding variable, bucketsize=10, dim=8 |
|("string",10,True)| 8 |Sparse embedding variable, bucketsize=10,dim=8|
|("string",None,True)| 8| Sparse dynamic embedding variable, dim=8 |
| "int" |None| Continues numeric tensor |
| ("int",10) | 8 | Embedding variable, bucket size=10, dim=8 |
| "float" |None/0| Continues numeric tensor |
"""
@property
def feature_spec(self):
"""
仅在和TF NN模型结合时使用,返回一个FeatureSpec对象。
"""
顶点Decoder¶
顶点的Decoder有以下几种形式。
import graphlearn as gl
# schema = (id int64, weight double)
gl.Decoder(weighted=True)
# schema = (id int64, label int32)
gl.Decoder(labeled=True)
# schema = (id int64, attributes string)
gl.Decoder(attr_type={your_attr_types}, attr_delimiter={you_delimiter})
# schema = (id int64, weight float, label int32)
gl.Decoder(weighted=True, labeled=True)
# schema = (id int64, weight float, attributes string)
ag.Decoder(weightd=True, attr_type={your_attr_types}, attr_delimiter={you_delimiter})
# schema = (id int64, label int32, attributes string)
gl.Decoder(labeled=True, attr_type={your_attr_types}, attr_delimiter={you_delimiter})
# schema = (id int64, weight float, label int32, attributes string)
gl.Decoder(weighted=True, labeled=True, attr_type={your_attr_types}, attr_delimiter={you_delimiter})
边Decoder¶
边的Decoder有以下几种形式。
import graphlearn as gl
# schema = (scr_id int64, dst_id int64)
gl.Decoder()
# schema = (src_id int64, dst_id int64, weight float)
gl.Decoder(weighted=True)
# schema = (src_id int64, dst_id int64, label int32)
gl.Decoder(labeled=True)
# schema = (src_id int64, dst_id int64, attributes string)
gl.Decoder(attr_type={your_attr_types}, attr_delimiter={you_delimiter})
# schema = (src_id int64, dst_id int64, weight float, label int32)
gl.Decoder(weighted=True, labeled=True)
# schema = (src_id int64, dst_id int64, weight float, attributes string)
gl.Decoder(weightd=True, attr_type={your_attr_types}, attr_delimiter={you_delimiter})
# schema = (src_id int64, dst_id int64, label int32, attributes string)
gl.Decoder(labeled=True, attr_type={your_attr_types}, attr_delimiter={you_delimiter})
# schema = (src_id int64, dst_id int64, weight float, label int32, attributes string)
gl.Decoder(weighted=True, labeled=True, attr_type={your_attr_types}, attr_delimiter={you_delimiter})
使用示例¶
假设数据源如下表1,表2,表3所示。
表1 item顶点表
| id | feature |
|---|---|
| 10001 | feature1:1:0.1 |
| 10002 | feature2:2:0.2 |
| 10003 | feature3:3:0.3 |
表2 user顶点表
| id | feature |
|---|---|
| 123 | 0.1:0.2:0.3 |
| 124 | 0.4:0.5:0.6 |
| 125 | 0.7:0.8:0.9 |
表3 user-item边表
| src_id | dst_id | weight |
|---|---|---|
| 123 | 10001 | 0.1 |
| 124 | 10001 | 0.2 |
| 124 | 10002 | 0.3 |
对item顶点表构建item_node_decoder,对user顶点表构建user_node_decoder,边表构建edge_decoder,代码如下。
import graphlearn as gl
item_node_decoder = gl.Decoder(attr_types=["string", "int", "float"])
user_node_decoder = gl.Decoder(attr_types=["float", "float", "float"])
edge_decoder = gl.Decoder(weighted=True)
对每一个数据源构建完Decoder之后,在图中加入数据源,并指定对应的Decoder,详见图对象 。
Decoder和NN模型结合¶
attr_types, attr_dims¶
一般的,Decoder只需要描述weighted, labeled, attr_types, attr_delimiter,即可将图数据解析加载到图中。
GraphLearn支持原始图数据中的顶点或边包含int、float、string 三种类型的特征,每种类型在NN模型中又有不同的表现形式。例如,int类型的特征即可当成连续的值来用,也可做为离散的id。 string类型的特征即可以为单值,也可以包含个数不定的多值。特征的定义需要在添加图数据源时描述清楚,后续便可通过GraphLearn提供的接口无缝转换,进而对接GNN算法。
因此,与神经网络结合时,attr_types和attr_dims需要做以下处理。
attr_types中string属性建议hash成int,即将"string"变为tuple类型("string", bucket_size)。string类型的属性比较难处理,通常做法是先将string通过hash映射到int,再把int编码成embedding。GL对string类型的属性做了特别扩展,即支持在图数据初始化阶段把string转成int。 此时,attr_types参数中的"string"需要变为tuple类型("string", bucket_size),bucket_size表示被转换到的int空间大小。若做此转换,后续访问时统一为int类型的attributes(包括条件负采样时)。 除了简化后续操作以外,该转换也会大大降低内存开销。- 离散属性需要指定
attr_dims。 在和TF的GNN模型结合时,数据的每一列属性会经过feature column,表达成向量。因此,在结合TF模型的代码中,Decoder不仅需要表达每一列属性原始输入类型attr_types,还应该描述离散属性如何编码为Embedding向量。具体地,attr_dims需要填写对应位置属性的Embedding维度。我们将attr_type和对应attr_dim表达属性的所有情况列举在Decoder类的参数注释中,以下是几个常用的示例。
case1:只有 float 特征。
# 20个float特征
# 下面user顶点的向量维度为20
decoder = gl.Decoder(attr_types=['float'] * 20)
# 都是float属性时,不需要指定attr_dims
g = gl.Graph()
g.node(source=file_path, node_type='user', decoder=decoder)
case2:把 int 特征当成连续特征来用。
# 1个float、2个int特征,int会被当做连续特征来处理
# 下面user顶点的向量维度为1 + 1 + 1 = 3
decoder = gl.Decoder(attr_types=['float', 'int', 'int'])
g = gl.Graph()
g.node(source=file_path, node_type='user', decoder=decoder)
case3:把 int 特征当成离散特征来用。
# 1个float、2个int特征,第一个int当做连续特征处理,第二个int作为bucket大小为1000的id处理
# 其中,id化的int将要被映射到维度为16的向量空间
# attr_dims长度必须与attr_types一致,非id类特征对应的位置填None即可
# 下面user顶点的向量维度为1 + 1 + 16 = 18
decoder = gl.Decoder(attr_types=['float', 'int', ('int', 1000)]
attr_dims=[None, None, 16])
g = gl.Graph()
g.node(source=file_path, node_type='user', decoder=decoder)
case4:单值 string 特征,即原始数据类型为 string ,首先hash成 int ,再作为离散特征处理。
# 2个string、1个int特征,分别作为bucket大小为500、800、1000的id处理
# 三类id将要被映射到维度为8、12、16的向量空间
# 下面user顶点的向量维度为8 + 12 + 16 = 36
decoder = gl.Decoder(attr_types=[('string', 500), ('string', 800), ('int', 1000)]
attr_dims=[8, 12, 16])
g = gl.Graph()
g.node(source=file_path, node_type='user', decoder=decoder)
case5:多值 string 特征,即原始数据类型为 string ,值以 , 分隔,每个值再作为单值 string 处理。
# 2个string特征,其中第二个为多值特征,多值以逗号分割,每个值将被当做bucket大小为800的id处理
# 两类特征将要被映射到维度为8、12的向量空间,其中多值特征的结果为每个值向量化后的加和
# 下面user顶点的向量维度为8 + 12 = 20
decoder = gl.Decoder(attr_types=[('string', 500), ('string', 800, True)]
attr_dims=[8, 12])
g = gl.Graph()
g.node(source=file_path, node_type='user', decoder=decoder)
以上以顶点特征为例进行说明,同样适用于边特征。